How can you download public sequencing data deposited in the NCBI Sequence Read Archive (SRA) into a Galaxy history for analysis?
The Sequence Read Archive (SRA) is the primary archive of unassembled reads operated by the US National Institutes of Health (NIH).
SRA is a great place to get the sequencing data that underlie publications and studies. The study we are interested in for this tutorial is one on sequencing of SARS-CoV-2 viral isolates that were obtained in the Boston area in the first months of the COVID-19 pandemic.
So lets see how we can find its raw data in the SRA, and how we can get some of that data into Galaxy to analyze it.
The Acknowledgments section of the publication mentions that raw reads from the study have been deposited in the SRA under BioProject PRJNA622837 so that’s going to be our starting point.

PRJNA622837[BioProject]
PRJNA622837[BioProject] AND RNA-Seq[Strategy]
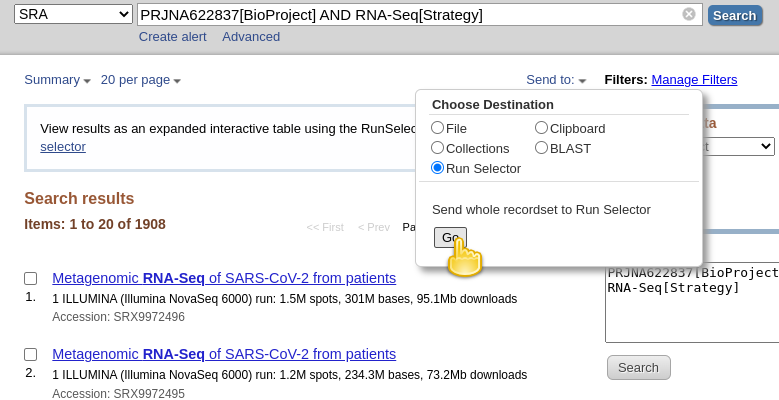
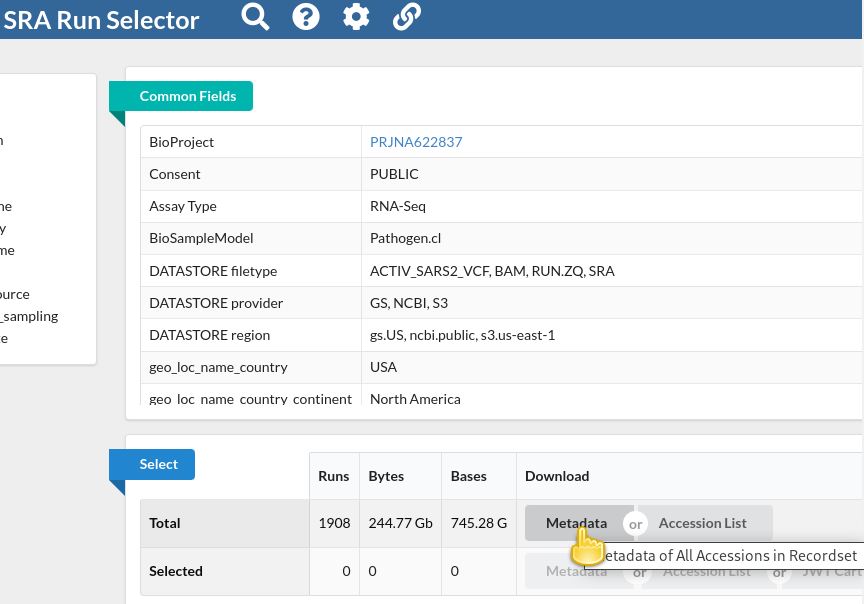
NOTE!!! Note that the file we just downloaded is not sequencing data itself. Rather, it is metadata describing the data itself
NOTE! Please, use
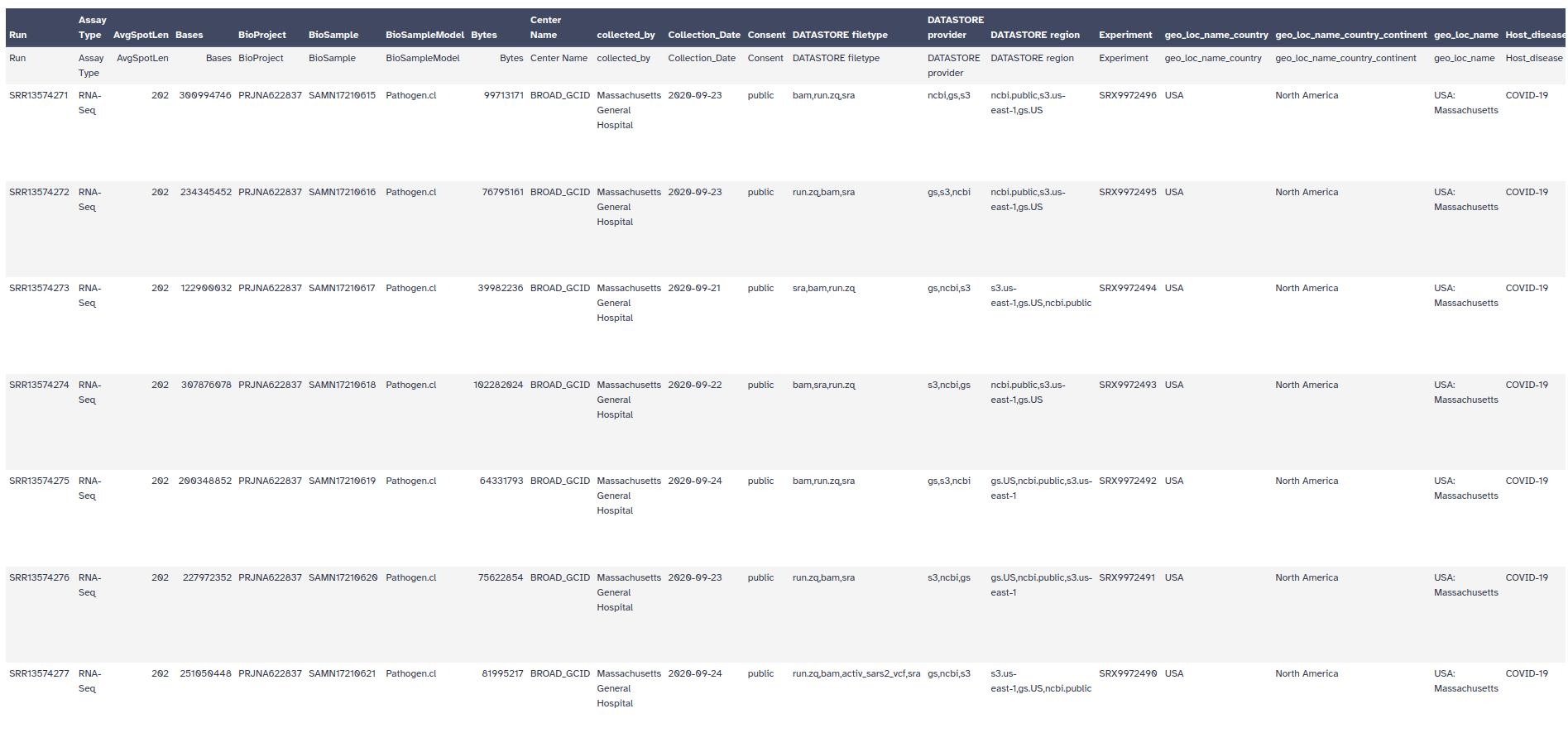
In Galaxy, it is rather easy to perform further filtering of the metadata records. For example, the publication mentions that the authors analyzed samples collected between 4 March and 9 May 2020,
If you inspect the metadata, you should see a column Collection_Date. That looks useful!
Filter data on any column using simple expressions tool with following parameters:
So now we are down to sequencing runs from the same date range as studied in the publication: though we still have more runs than samples discussed in the publication.
Note, however, that the publication talks about assembled genomes, and it is possible that some of the sequencing runs listed in our metadata do not contain good enough data to assemble any SARS-CoV-2 genome information, or it could be that some viral samples got sequenced in several sequencing runs to obtain enough data.
We suggest to continue with just the following two interesting datasets: SRR11954102 and SRR12733957. So let’s pull their identifiers out of the metadata file.
Select lines that match an expression Tool with following datasets:
Filter toolAdvanced Cut Tool with following datasets:
Select toolAt this point, you should have a dataset with just two lines and a single column with this content:
SRR12733957
SRR11954102
Now that we have our identifiers of interest extracted, we are ready to download the actual sequencing data. Since this is a very common need Galaxy offers a dedicated tool for the purpose of downloading sequencing data from the SRA identified via its run accession.
Faster Download and Extract Reads in FASTQ Tool with the following parameters:
CutSeveral entries should have been created in your history panel when you submitted the previous job:
When the tool run is finished, you should find that only the Pair-end data collection contains any sequencing data, which makes sense as both samples have been paired-end sequenced on the Illumina platform.
Now, it’s your turn! Retrieve the BioProject ID from this article and upload the datasets to a new history in Galaxy.
In order to save time, we have pre-selected the samples that appeared to be the most significant.
SRR18739533
SRR18739534
SRR18739542
SRR18739550
SRR18739557
SRR18739561
SRR18739563
SRR18739566
SRR18739571