Genome annotation with Prokka
How can we annotate a bacterial genome? How can we visualize annotated genomic features?
Genome annotation is the comprehensive process of deciphering the genetic blueprint of an organism,
identifying its various elements, and assigning meaning to those elements.
It involves two primary components:
- Structural Annotation: Positions of genomic features along the genome, ie. determining the physical organization of the genome
- Gene Prediction: Identifying the locations and boundaries of genes within the DNA sequence.
- Intron-Exon Boundaries: Defining the positions of introns and exons in genes.
- Promoters and Regulatory Elements: Identifying regions responsible for gene regulation, such as promoters, enhancers, and transcription factor binding sites.
- Non-Coding RNAs: Discovering non-coding RNA elements, including tRNAs, rRNAs, microRNAs, and long non-coding RNAs.
- Functional Annotation: Assigning functions to those features, ie. etermining the biological roles and functions of the annotated elements.
- Protein Function: Assigning functions to proteins encoded by the genes.
- Metabolic Pathways: Linking genes to specific metabolic pathways, providing insights into the organism’s biochemical capabilities.
- Gene Ontology (GO) Terms: Categorizing genes based on their molecular functions, biological processes, and cellular components using the Gene Ontology database.
- Homology and Orthology: Establishing relationships between genes in the annotated genome and those in other organisms, allowing for comparative genomics.
In this section we will use a software tool called Prokka to annotate a draft genome sequence.
Prokka is a wrapper: it collects together several pieces of software
(from various authors), and so avoids “re-inventing the wheel”.Prokka finds and annotates features (both protein coding regions and RNA genes, i.e. tRNA, rRNA) present on a sequence.Prokka uses a two-step process for the annotation of protein coding regions:
- protein coding regions on the genome are identified using Prodigal;
- the function of the encoded protein is predicted by similarity to proteins in one of many protein or protein domain databases.
Prokka is a software tool that can be used to annotate bacterial, archaeal and viral genomes quickly, generating standard output files in GenBank, EMBL and gff formats.
Go Up
Importing the data into Galaxy
NOTE! Please, use:
Prokka requires assembled contigs.
- Create a new history
- Upload datasets
https://zenodo.org/record/1156405/files/contigs.fasta
Go Up
Annotate the genome
Prokka Tool with the following parameters (leave everything else unchanged):
- contigs to annotate: contigs.fasta
Examine the output
Once Prokka has finished, examine each of its output files.
GFF: Annotation in GFF3 format, containing both sequence and annotations: all of the information about the features annotatedGBK: Standard GenBank file. As GFF Ffile contain all of the information about the features annotated (in different format.).txt: Statitstics relating to the features annotated..faa: The protein sequences of the genes annotated (FASTA)..ffn: The nucleotide sequences of the genes annotated (FASTA).
Go Up
View annotated features in JBrowse
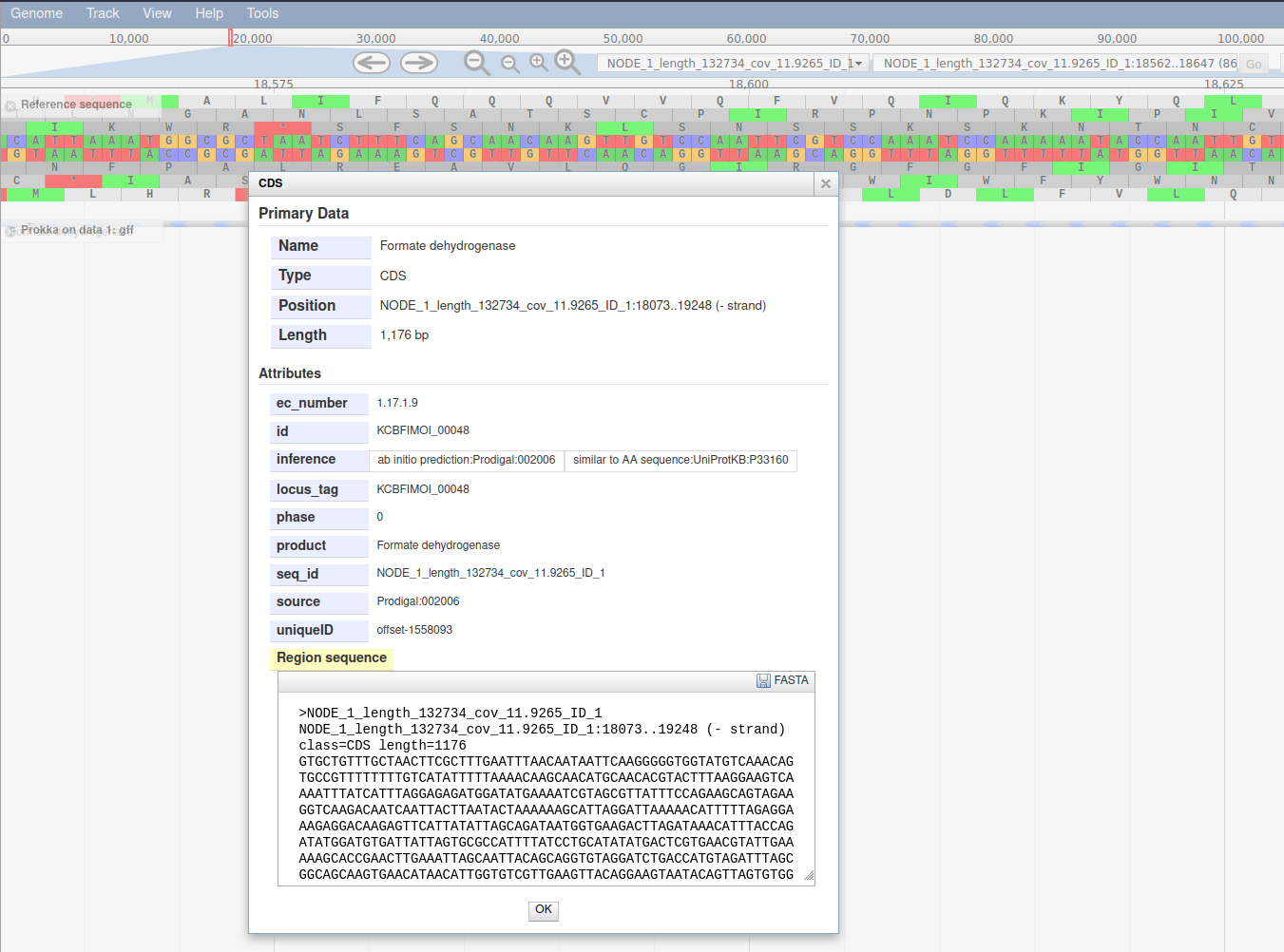
Now that we have annotated the draft genome sequence, we would like to view the sequence in the JBrowse genome viewer.
JBrowse Tool with the following parameters
- Reference genome to display: Use a genome from history
- Select the reference genome: fna output of
Prokka Tool
- Genetic Code: 11: The Bacterial, Archaeal and Plant Plastid Code
- In Track Group:
- Insert Track Group
- Track Category: gene annotations
- Track Type: GFF/GFF3/BED Features
- GFF/GFF3/BED Track Data: gff output of
Prokka
Click on Insert Track Group
- Inspect the output
- Display all the tracks and practice maneuvering around
- Click on the tick boxes on the left to display the tracks
- Select contig 1 in the drop down box. You can only see one contig displayed at a time.
- Zoom by clicking on the
plus and minus buttons.
- Right click on a gene/feature annotation (the bars on the annotation track), then select
View Details to see more information.
- gene name
- product name
- you can download the FASTA sequence by clicking on the disk icon
Go Up
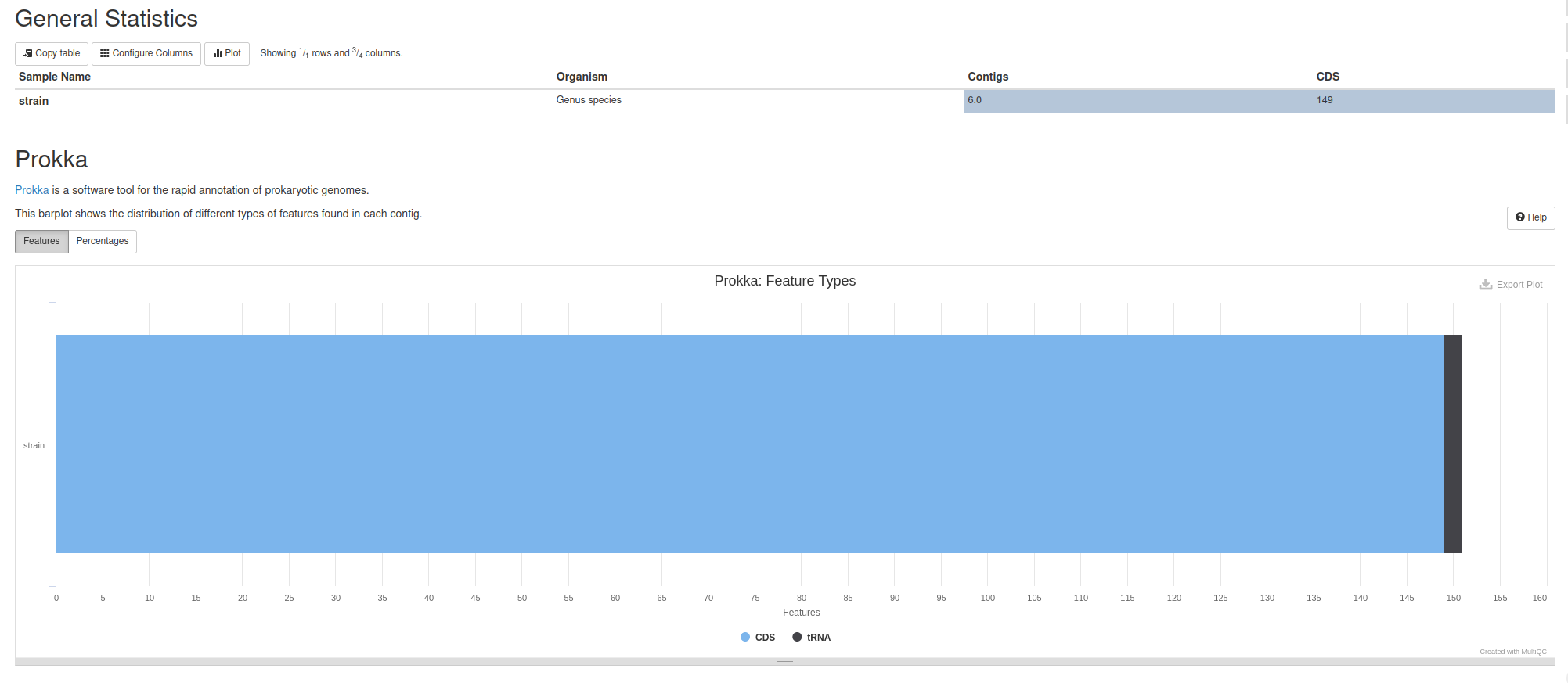
MultiQC Report
MultiQC tool with following parameters
- In “Results”:
- Insert Results
- Which tool was used generate logs?: Prokka
- *In “Prokka Output”:
- Prokka Output: Prokka .txt
- Report title: Genome Annotation Report
Go Up
Hands-On
Now, it’s your turn!
Go Up

