Galaxy at a Glance
A brief introduction to Galaxy. What is Galaxy? Why should you use Galaxy? How do you use Galaxy?
Galaxy at a Glance

Data Intensive analysis for everyone
- Web-based platform for computational biomedical research
- Developed at Penn State, Johns Hopkins and G. Washington universities with substantial outside contributions
- Open source under Academic Free License
- More than 11,900 citations
- More than 170 public Galaxy servers
- Many more non-public
- Both general-purpose and domain-specific
Core values
- Accessibility
- Users without programming experience can easily specify parameters, run tools, workflows and parse/filter data
- Reproducibility
- Galaxy captures information so that any user can repeat and understand a complete computational analysis
- Transparency
- Users can share or publish their analyses (histories, workflows, visualizations)
- Pages: online Methods for your paper
Go Up
User Interface
Main Galaxy interface
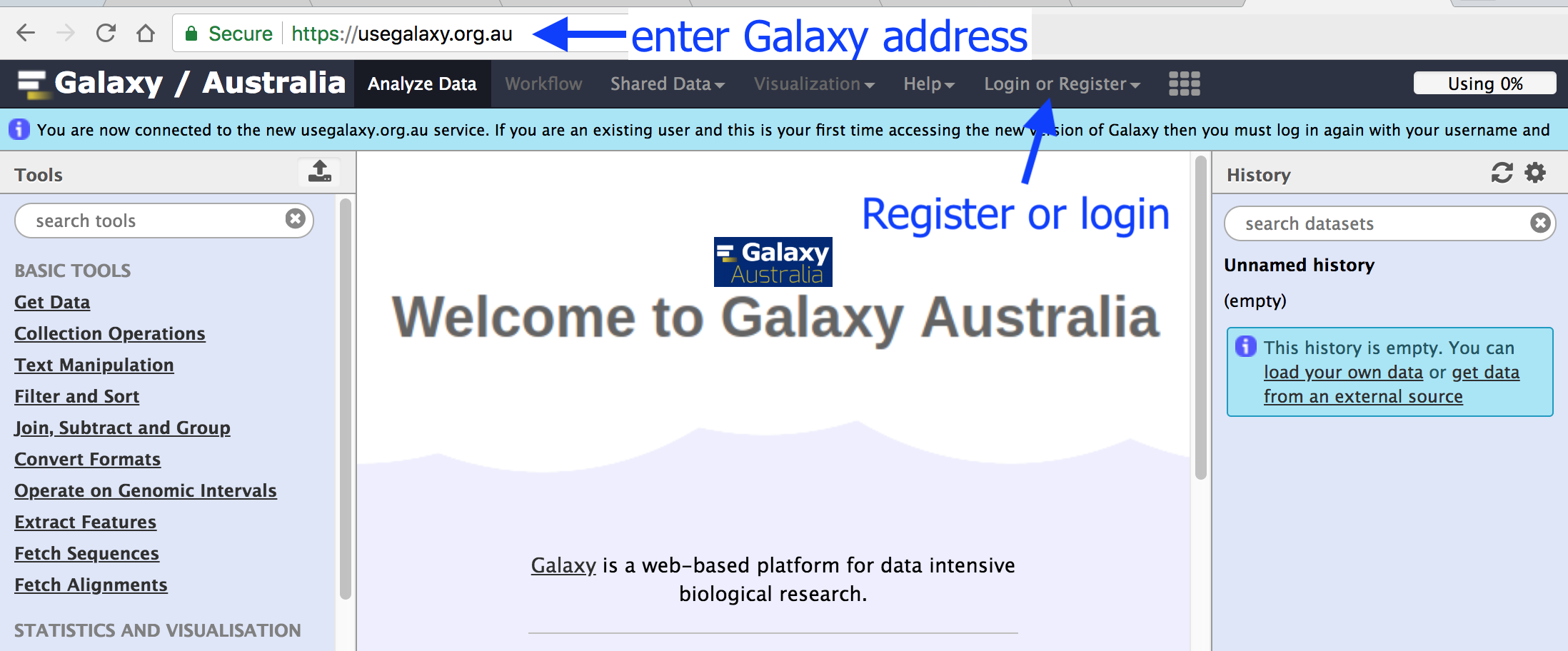
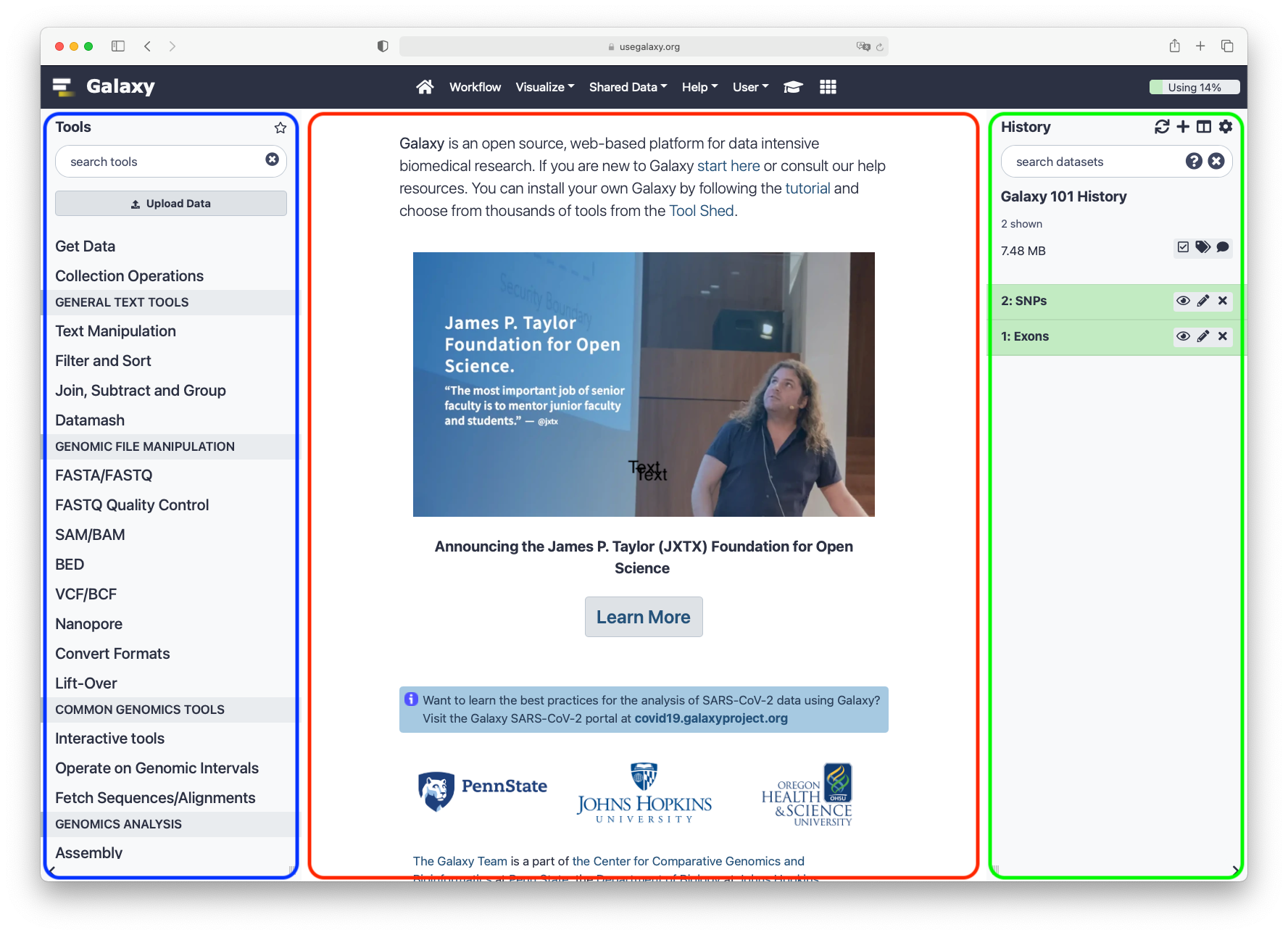
Home page divided into 3 panels
Go Up

- (Analyze Data) - go back to the 3-panels homepage
- Workflow - access existing workflows or create new one using the editable diagrammatic pipeline
- Visualize - create new visualisations and launch Interactive Environments
- Shared data - access data libraries, histories, workflows, visualizations and pages shared with you
- Help - links to Galaxy Biostar (Q&A), Galaxy Community Hub (Wiki), and Interactive Tours
- User - your preferences and saved histories, datasets, and pages
Go Up
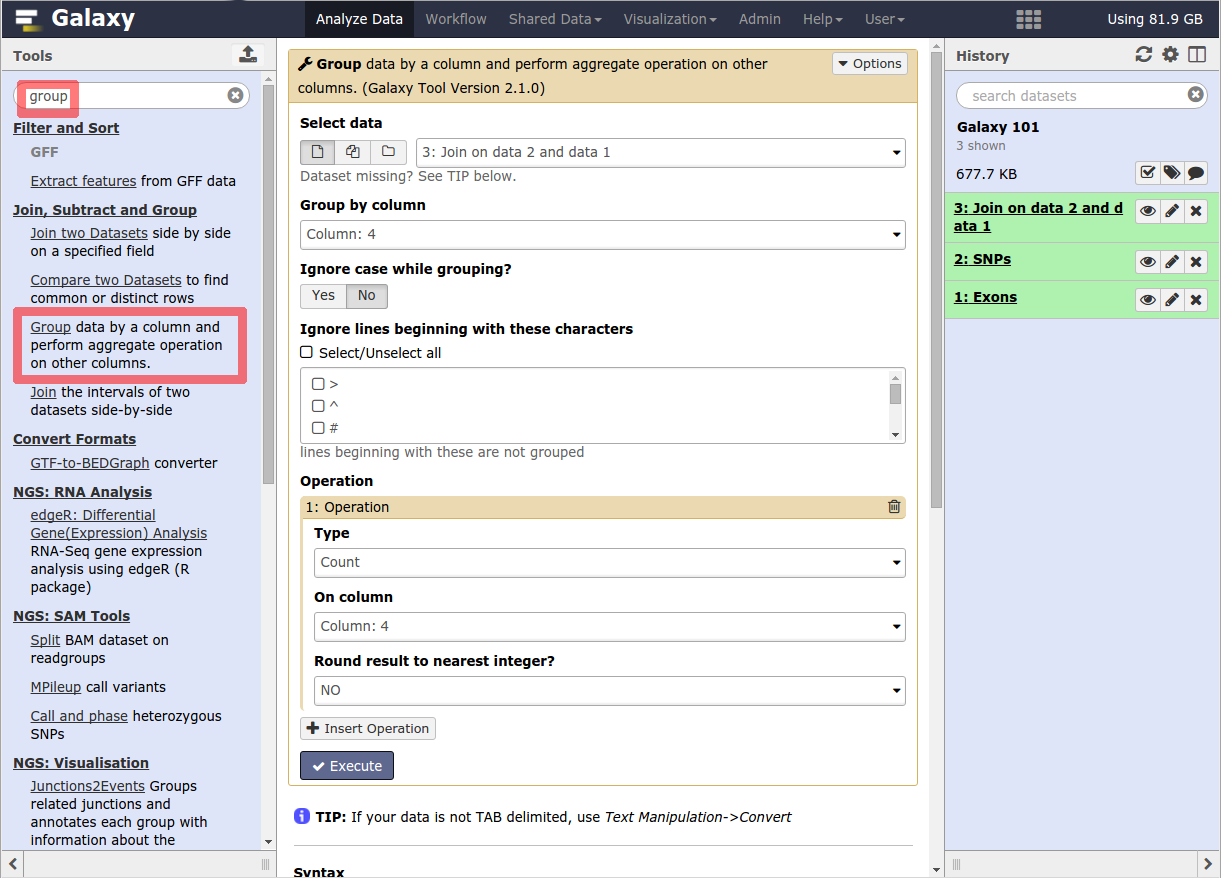
The tool search helps in finding a tool in a crowded toolbox
|
A tool form contains:
- input datasets and parameters
- help, citations, metadata
- an `Execute` button to start a job,
which will add some output datasets to the history
|
|
Go Up
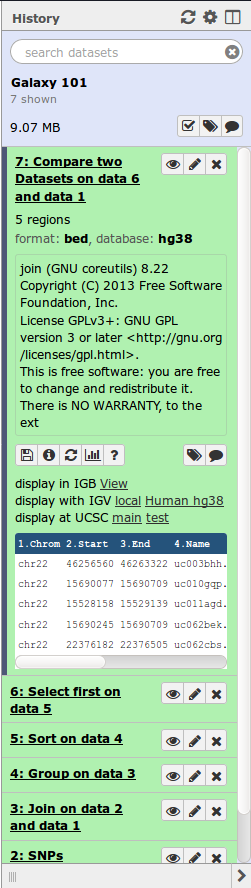
History
|
Location of all your analyses
- collects all datasets produced by tools
- collects all operations performed on the data
For each dataset (the heart of Galaxy’s reproducibility), the history tracks
- Name, format, size, creation time, datatype-specific metadata
- Tool id and version, inputs, parameters
- Standard output (`stdout`) and error (`stderr`)
- State: waiting; running;
success; failed
- Hidden, deleted, purged (== permanently deleted)
|
Go Up
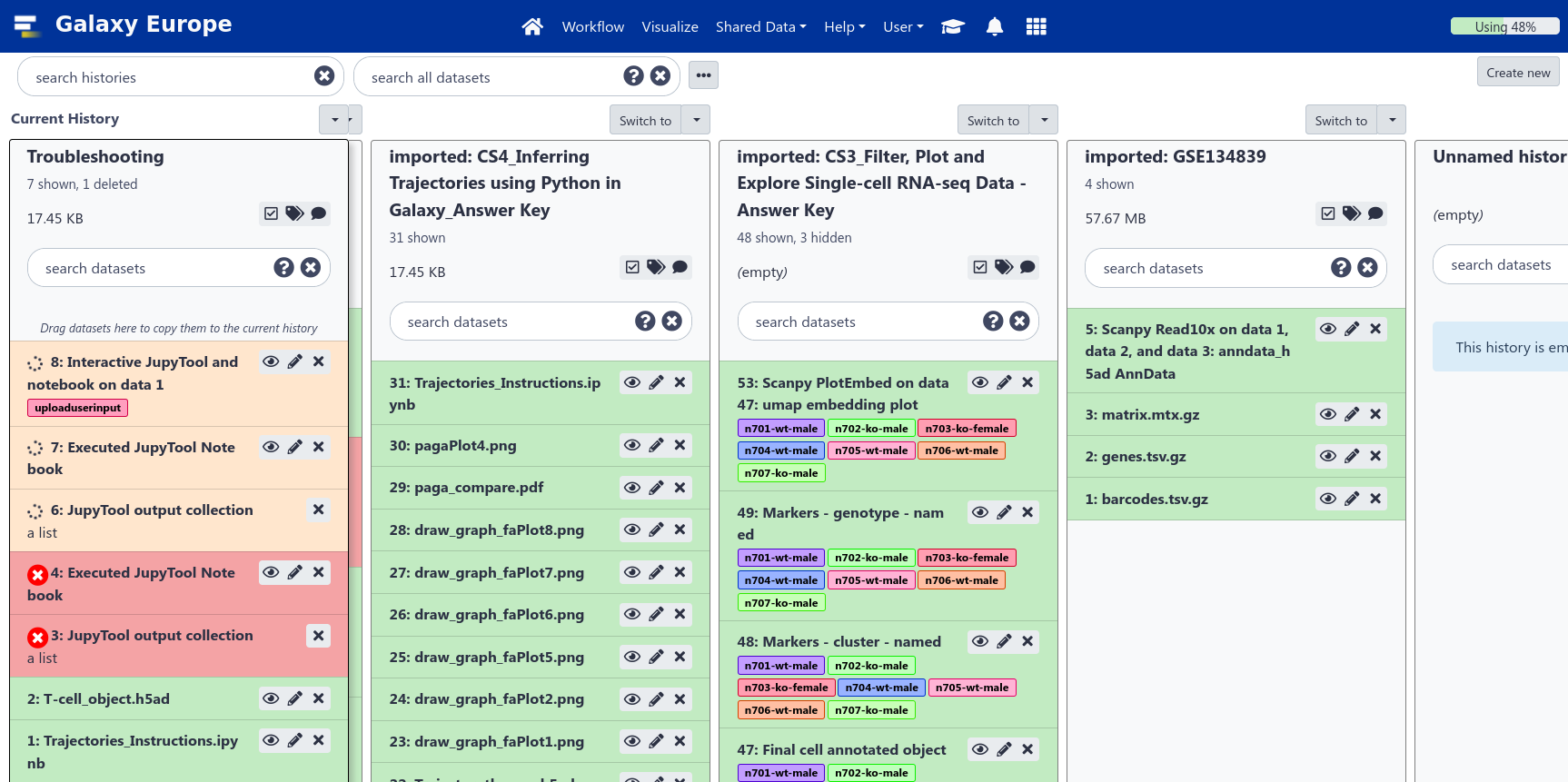
Multiple histories
- You can have as many histories as you want
- Each history should correspond to a different analysis
- and should have a meaningful name
Go Up
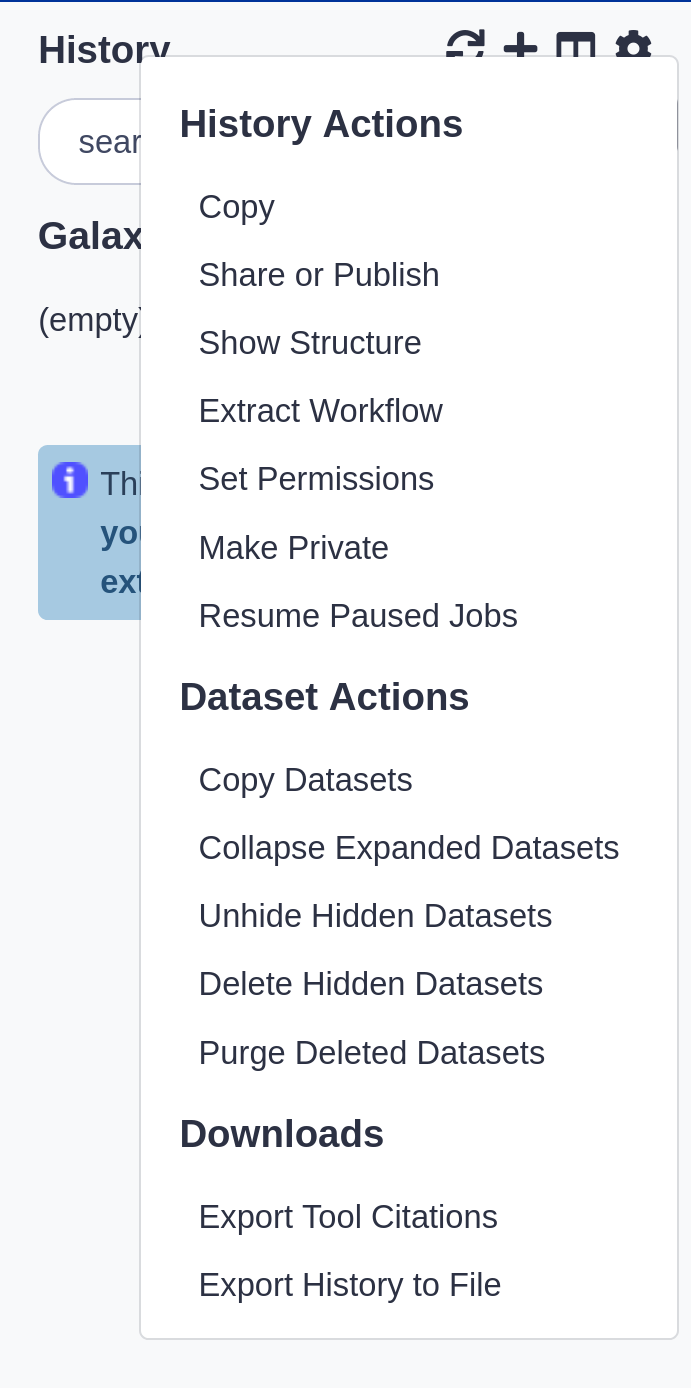
History behavior is controlled by the History options
Most options are self explanatory
|
- Create New history will not make your current history disappear
- To see all of your histories, use the history switcher
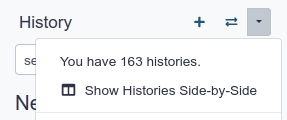
- You can Copy Datasets from one history to another
|
Go Up
Loading data
Importing data
- Copy/paste from a file
- Upload data from a local computer
- Upload data from internet
- Upload data from database queries
- UCSC, BioMart, ENCODE, modENCODE, Flymine etc.
- Download shared data from public libraries or shared Data libraries, Histories, Workflows, Visualizations, and Pages on https://usegalaxy.org/
- Upload data from FTP (>2GB)
See Tutorial
Go Up
Datatypes
- When uploading, datatype can be automatically detected or assigned by user
- For datasets produced by a tool, the datatype is assigned by the tool
- Tools only accept input datasets with the appropriate datatypes
- You can change the datatype in 2 ways:
- Edit Attributes -> Datatype (to fix a wrongly assigned datatype)
- Edit Attributes -> Convert Formats (converts the original dataset)
Go Up
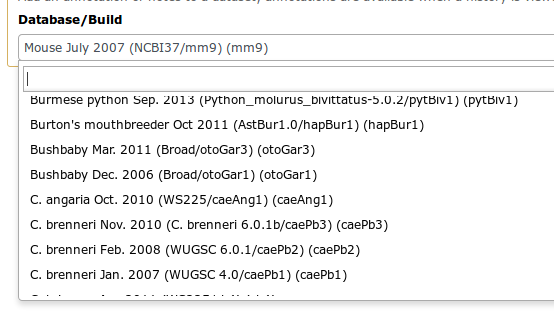
Reference genomes
- Genome build specifies which genome assembly a dataset is associated with
- Genome build can be automatically detected or assigned by user
- User can define their own custom genome build
- New genome assembly can be added by the site Galaxy admin
Go Up
Data Libraries
Provide a way to conveniently share Galaxy datasets within a group of Galaxy users or with everybody that has access to a specific instance of Galaxy.
- Can import data from filesystem without duplicating it.
- Can import whole directories preserving the folder structure.
- The dataset’s size does not count towards user’s quota.
- Every dataset in the library is stored only once no matter how many users are using it in their histories.
- Uses roles and groups to control permissions on library/dataset level.
- Only admins can create libraries.
Go Up
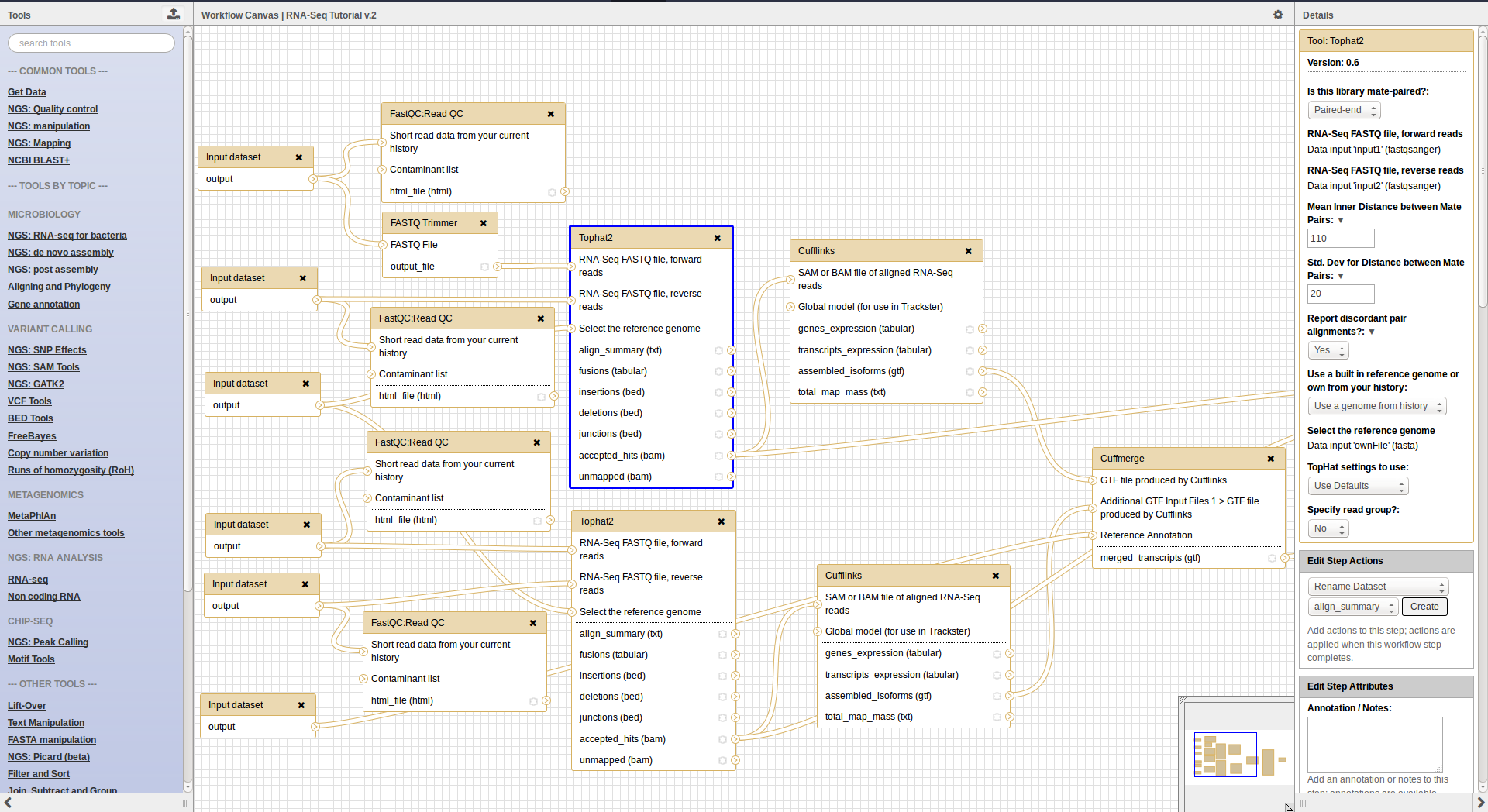
Workflows
Workflow interface
Go Up
Workflows
- Can be extracted from a history
- Allow to easily convert an existing history into an analysis workflow
- Can be built manualy by adding and configuring tools using the workflow canvas
- Can be imported using an existing shared workflow
Go Up
Why would you want to create workflows?
- Re-run the same analysis on different input data sets
- Change parameters before re-running a similar analysis
- Make use of the workflow job scheduling
- job is submitted as soon as its inputs are ready
- Create sub-workflows: a workflow inside another workflow
- Share workflows for publication and with the community
Go Up
Data sharing
- You can share your Galaxy items - histories, workflows, visualizations, and pages - with other people in three different ways:
- Directly using a Galaxy account’s email addresses on the same instance
- Using a web link, with anyone who knows the link
- Using a web link and publishing it to make it accessible to everyone from the Shared Data menu
Go Up










